Setting Up Moodle on AWS
Seed was recently engaged by one of our customers to migrate their existing onsite Moodle set up to the cloud on Amazon Web Services.
Moodle is a Course Management System (CMS), also known as a Learning Management System (LMS) or a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE). It is a free web application that educators can use to create effective online learning sites.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a collection of remote computing services that together make up a cloud computing platform, offered over the Internet by Amazon.com.
Since cloud is gaining more and more momentum as an alternative to having onsite servers for many organisations and Moodle being a very popular LMS, we thought writing a blog about it would be a good idea.
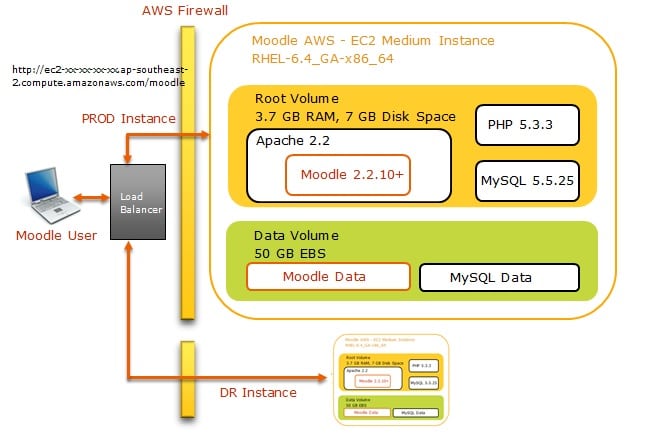
The above diagram shows the main components of the Moodle set up on AWS. The details of the components are described in the next section.
Moodle-AWS Components
As mentioned previously, AWS is a collection of remote computing services and the most central and well-known of these services are Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3.
EC2 Instance
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
Amazon EC2 was used to launch a 64-bit Redhat 6.4 instance from a pre-configured, template called an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) in Asia-Pacific Sydney region (ap-southeast-2b). An AMI is a special type of pre-configured operating system and virtual application software which is used to create a virtual machine within the EC2.
The M1 Medium EC2 Instance was used for the Moodle and has the following specifications; 3.75 GB of memory, 2 EC2 Compute Units (1 virtual core with 2 EC2 Compute Units each), and 64-bit platform
Security and network access to the Moodle EC2 instance is defined through AWS own firewall, where a rule defining which ports are opened/accessible, is attached to the EC2 instance.
The EC2 Instance can be started/stopped, terminated, and monitored through the AWS Admin Console.
An elastic IP address was reserved and associated with the Moodle EC2 instance. Elastic IP addresses are static IP addresses designed for dynamic cloud computing. This makes sure that Moodle is accessible through the same url associated with the elastic IP address after an instance restart.
Root Volume
When an EC2 instance is launched, a root or boot volume is automatically created. This root volume would be created based on the AMI used. In this case, a basic Redhat 6.4 instance with 7 GB root volume was created. Once the instance was up and accessible through SSH, Apache, MySQL, PHP and Moodle were installed.
Data Volume
Once the instance was created, an Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volume was created and attached to it. An EBS volume offers persistent storage for Amazon EC2 instances and would serve as the Data Volume for Moodle and MySQL. This 50 GB volume was mounted as /data on the root volume. The whole point of having the Data Volume is to have a more manageable data layer and also for easy data backup.
Note1
In order to ensure that the system auto mounts the volume on restart, the following entry needs to be added to /etc/fstab.
/dev/xvdj /data ext4 defaults 0 0
Note2
After attaching the data volume to the Moodle instance, we found that upon doing an instance restart, we could no longer connect to the instance through SSH. The reason SSH connection does not work, is due to certain Redhat Instances corrupting the file /etc/ssh/sshd_config by wrongly adding duplicate entries at the end of the file.
In order to restore the SSH, attach the root volume to another working instance as a secondary volume and then remove the duplicate entries in /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
System Configurations
Redhat Environment
Redhat 6.4 comes with SELinux set to ‘Enforcing’ mode which prevents the installation of MySQL and Moodle data directory outside the root volume directory. Hence SELinux was set to ‘Permissive’ mode by modifying /etc/selinux/config as follows
set SELINUX=permissive
MySQL
MySQL 5.5 was installed and configured to have its data directory on the Data Volume and support Moodle.
The following SQL queries were used to create the Moodle DB
CREATE DATABASE moodle CHARSET ‘utf8’;
GRANT SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,CREATE,DROP,INDEX,ALTER ON moodle.* TO moodle@localhost IDENTIFIED BY ‘xxxx’;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Note 1
In order to move mysql data directory to the data volume, the following steps were taken
· Stop MySQL
/etc/init.d/mysql stop
· Create new directory
mkdir -p /data/mysql
· Copy or move mysql content to new directory
cp -R /var/lib/mysql/* /data/mysql/
· chown -R mysql:mysql /data/mysql
· vim /etc/my.cnf
o [client]
o socket = /data/mysql/mysql.sock
o [mysqld]
o datadir=/data/mysql
o socket = /data/mysql/mysql.sock
· Start MySQL
/etc/init.d/mysql start
Note 2
#Moodle does not support the ‘statement’ format so uncomment the following line in /etc/my.cnf
binlog_format=mixed
Moodle and Apache
Moodle installation
Moodle runs within Apache (/etc/httpd/) and the Moodle installation directory is /var/www/html/moodle.
· Download the required Moodle version and unzip it.
· Move the unzipped folder as moodle to Apache root directory (/var/www/html)
· In the moodle directory, copy config-dist.php file to config.php
· Access moodle through the wwwroot url specified
The config.php was modified as follows;
$CFG->dbname = ‘moodle’; // database name
$CFG->dbuser = ‘moodle’; // database username
$CFG->dbpass = ‘xxxx’; // database password
$CFG->dboptions = array(
‘dbpersist’ => false
‘dbsocket’ => ‘/data/mysql/mysql.sock’, // MySQL data directory
‘dbport’ => ”
);
$CFG->wwwroot = ‘http://ec2-xx-xx-xx-xx.ap-southeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com/moodle’;
$CFG->dataroot = ‘/data/moodledata’;
Note
Make sure the following dependencies are installed
php-xml php-pdo php-soap php-common php-cli php-mbstring php-bcmath php-imap php-gd yum php-pear memcached php-mcrypt php-xmlrpc php-intl
Moodle Backup and DR
DR
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) was created from the production instance and stored in Amazon S3.
Amazon S3 provides a simple web services interface that can be used to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web. This AMI of the production instance is to be used to create a new Moodle instance in case the current one gets corrupted.
This AMI was also used to create Moodle DR Instance in a different zone in the Asia Pacific Sydney Region (ap-southeast-2a is used for DR while ap-southeast-2b is used for PROD) to be used as Disaster Recovery scenario. By having the DR instance in a different availability zone we are ensuring against datacentre loss within Australia.
Backup
A script was written so that a snapshot of the data volume is created every night (a cron job was added in /etc/crontab) and from which a data volume with the latest data can be restored and attached to the instance. The snapshots are also store on Amazon S3.
Note
The script makes calls to the Amazon API tools.

